
Noninvasive & Long-Acting Thermoresponsive Hydrogel for Sustained Ocular Drug Delivery
This invention is a noninvasive ocular delivery system consisting of drug-loaded, biodegradable microparticles suspended in a liquid thermoresponsive hydrogel that solidifies upon contact with the eye. It provides sustained therapeutic release for up to one month, eliminating the need for frequent daily eye drops and invasive clinical injections.
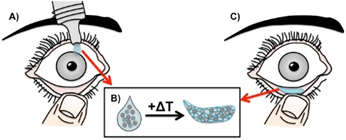
Description
The technology utilizes a "drop-to-gel" mechanism where a liquid suspension is self-administered to the lower fornix of the eye. Upon reaching physiological temperature (typically above 32-34°C), the thermo-responsive polymer, such as poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAAm), undergoes a phase transition to form a solid, biocompatible hydrogel depot. This gelled member remains in the eye, securely holding the therapeutic payload in place. Embedded within this hydrogel matrix are spray-dried microparticles made from biodegradable polymers like PLGA. These microparticles are engineered to release active agents, such as cysteamine or brimonidine, at a controlled rate through diffusion and polymer degradation. This dual-stage delivery system ensures a steady therapeutic concentration over extended periods, ranging from five days to over a month and can be easily removed by the user with tweezers or saline once the treatment cycle is complete.Applications
- Glaucoma Management: Sustained delivery of agents that lower intraocular pressure (IOP), such as brimonidine or prostaglandins.- Cystinosis Treatment: Long-term delivery of cysteamine to reduce cystine crystal formation in the cornea.
- Chronic Ocular Infections: Controlled release of antibiotics like moxifloxacin or vancomycin.
- Post-Operative Care: Delivery of anti-inflammatory steroids or immunosuppressants to manage recovery.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: Sustained release of comfort agents or immunosuppressants like cyclosporine.
Advantages
- Enhanced Patient Compliance: Replaces the need for multiple daily eye drops with a single weekly or monthly administration.- Noninvasive Administration: Offers a self-administered alternative to invasive clinical procedures like intravitreal or anterior chamber injections.
- Superior Stability: Maintains at least 90% of active drug content (e.g., cysteamine) for at least seven weeks, outperforming current commercial standards.
- Improved Permeability: Provides more efficient corneal permeability compared to traditional eye drops.
- Removable and Safe: The gelled depot is firm enough to be removed manually by the patient, and the materials used are biocompatible and biodegradable.
Invention Readiness
The technology has undergone extensive in vitro and ex vivo testing, demonstrating stable drug loading and efficient corneal permeability. In vivo studies in rabbit models have successfully validated the system's efficacy, showing statistically significant reduction in intraocular pressure over a 28-day period compared to standard topical drops. Further studies are needed to evaluate long-term safety in human subjects and to optimize the loading of diverse therapeutic classes for specific clinical indications.IP Status
https://patents.google.com/patent/US20220211632A1Related Publication(s)
Jimenez, J., Resnick, J. L., Chaudhry, A. B., Gertsman, I., Nischal, K. K., & DiLeo, M. V. (2022). Ocular biodistribution of cysteamine delivered by a sustained release microsphere/thermoresponsive gel eyedrop. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 624, 121992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121992
Jimenez, J., Washington, M. A., Resnick, J. L., Nischal, K. K., & Fedorchak, M. V. (2021). A sustained release cysteamine microsphere/thermoresponsive gel eyedrop for corneal cystinosis improves drug stability. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 11(5), 2224–2238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-020-00890-6
Bruk, L. A., Dunkelberger, K. E., Khampang, P., Hong, W., Sadagopan, S., Alper, C. M., & Fedorchak, M. V. (2020). Controlled release of ciprofloxacin and ceftriaxone from a single ototopical administration of antibiotic-loaded polymer microspheres and thermoresponsive gel. PLOS ONE, 15(10), e0240535. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240535
